1. NEED DEVELOPMENT SYSTEM
Development of the system may mean preparing a new system for replace
The old system or improve the overall system existing.
Need for Development of System:
• There is a problem (problem) that arise in the old system
The problems that arise can be:
· Irregularity
· Organizational growth
• To seize the opportunity (opportunities)
Information technology has developed so quickly
• The instructions (directives)
2 Destinion development systemat
Development means the system can arrange a new system to replace the old system as a whole or improve the existing system. The old system need to be replaced or repaired is because some things are as follows:
• The existence of the problems that arise in the old system. The problems that arise can be:
a. Irregularity
Irregularity in the old system caused the old system can’t operate in accordance with that expected. This irregularity may be operating inefficiently.
b. The growth of the organization
Growth of the organization must be the establishment of a new system. The growth of these organizations is the information needs of the area, the volume of data increases, changes in the new accounting principles.
• To capture the opportunities
Organization began to feel that information technology should be used to improve the provision of information so that it can support in the decision making process that will be done by management. Competitive in the market, the efficiency or speed of information that is not to determine the success or strategy plan and that plan has been developed to seize the opportunities that exist. If competitors can utilize, while the company can not take advantage of this technology, the opportunity will fall caption competition.
• The instructions
Preparation of the new system can also occur because of instructions from the top leadership or from outside organizations, such as government regulations.
3. Expected on the new system
Has been developed with the new system, the expected increase will occur, the increase in the new system.
• Performance
Improvement of the performance of the new system which will be most effective. Performance can be measured from the throughput and response time.
• Information
Improving the quality of information presented.
• Economy
Improvement of the benefits or the benefits or a decrease in the cost-reduction.
• Control
Detect and fix errors that occur and will occur.
• Efficiency
Improvement of operational efficiency.
• Services
Improvement of the services provided by the system.
4. SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT PRINCIPLES
• The system is developed for management
• The system developed is a large capital investment
Investment capital should consider 2 things:
1. 1. All alternatives should be investigated
2. 2. Investment should be the best value
• System developed need educated people who
Stages of work and tasks that must be made in the development process system
• The development of the system does not have to order
• Do not be afraid to cancel the project
• Documentation must be available to guide in the development of the system
5. System development life cycle
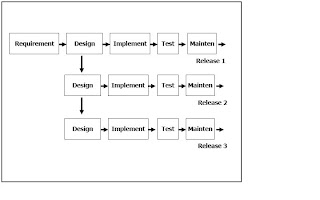
Waterfall Model
Contains a series of activities such as the process has been described above and presented in a separate process, such as the requirement specification, design implementation software, testing . After each step is defined, this step in the sign off and followed the development in the next step.
The steps that are important in this model is
- The analysis and specification
Services, goals and constraints resulting from consultation with users system. Then everything is made in the form that can be understood by users and staff developers.
- Design systems and software
Divide the system design process needs to be system software or hardware. The process produces an overall system architecture. Design software, including the functions of system software that may be in the form of the transformation in one or more programs that can be run.
- Implementation and unit testing
During this stage, the design software we realize as a complete program or program unit. Test units, including units that each test according to specification.
- Integration and system testing
Unit tested and integrated into the system that the program can complete requirements for the software has been met. After testing, the system was delivered to the customer
- Operation and maintenance
This phase is long. System installed and used. Maintenance, including correction of errors not found in the previous step. Improvements to the implementation of the system and increasing service needs of the new system as found.
RAD Model
- Rapid Application Development
- The development of s / w in sekuensial linier
- adaptation do high speed, can be made in pace with the development approach component-based
- If the data, clear analysis, and the scope of small
the RAD can be used with both - Often also called a 'high speed version' of waterfall model,
- Emphasis on development cycles a short
- RAD approach to follow the following phases;
- Business modeling, the flow of information from model with the function;
information is affecting business, who appear, who is issue, the information I given, Who processing? - Data modeling; Part of the modeling business defined in a set of data objects.
- The characteristics (attributes) of each object identified and related
- The process of modeling, the object data will be implemented on the business functions.
- Descriptions for the built additional modifications, deletion, or return the data object.
- Data modeling; Part of the modeling business defined in a set of data objects.
- The characteristics (attributes) of each object identified and related
- The process of modeling, the object data will be implemented on the business functions.
- Descriptions for the built additional modifications, deletion, or return the data object.
- Application generation, Conducting re-use components that have (if possible)
- Or make use of return components if required.
- Testing / turnover, the RAD emphasizes the use of return and program components are ready to test
Weakness RAD
- Model of the (project scale), resources requires good and solid
- Requires commitment developer and the same user to be completed quickly accordance with the plan
Spiral model
Spiral model describes the process as a spiral which is divided into 4 quadrants:
process in accordance with the cycle using the prototyping approach.
• Planning
namely the duties to plan, gather for the alternative system that will have • Risk Analysis
is to evaluate the alternatives based on the objectives and constraints. Included here to identify the certainty and risk
• Engineering
that is a task that is required to build one or more statements of this section
• Customer Evaluation.
Re-evaluate the system that was created with the customer
6.System development approach
• A structured approach versus classical approach (seen from the methodology used)
• Piecemeal approach versus system approach (seen from the target to be achieved)
• The bottom-up approach versus top-down approach (seen from how to determine the needs of the system)
• Total-system approach versus modular approach (seen from the way the developing)
• Great loop- approach versus evolutionary approach approach (seen from the technology that will be used)
A structured approach versus classical opponent approach
Classical approach
• Stages in SDLC-stage
• not to include users, system analysts put more emphasis
• The problem: the development of hard, expensive treatment, the possibility of error, success is less assured, the problems in the implementation of
Structured approach
• User involvement from the beginning to determine the needs of the system
• Using tools-tools such as data flow diagrams
Piecemeal approach versus system approach
Piecemeal approach
• Emphasizing on an application or event
• don’t override the overall target
System approach
• Viewing the system as a whole is unity
• Emphasizing the achievement of overall objectives
Bottom-up approach versus top-down approach
Bottom-up approach
• Starting from the bottom level of the operational
• It is the characteristics of classical
• Known by the term data-analysis
Top-down approach
• Starting from the top-level strategy planning
• It is the characteristics of structured
• Also known to the decision-analysis
Total-system approach versus modular approach
Total-system approach
• Develop a system simultaneously and comprehensively
• It is the characteristics of classical approach
Modular approach
• break a complex system into parts of a simple
• System to be developed on time, easy to understand and kept
• It is the characteristics of structured
Great loop- approach versus evolutionary approach approach
great-loop approach approach
• Develop a system simultaneously using the advanced technology
• At risk and spend a lot of high cost
evolutionary approach approach
• Applying advanced technology for application-specific applications
• Developed for the needs
• Save the cost and can follow the development of technology
7. Methodology, method and algorithm
• Methodology
Is methods used in science
• Method
A systematic way to grind
• Algorithm
Sort-order the procedure to solve a problem
8. Classification of development methodology
• Functional decomposition
– Emphasizing the breakthrough system subsystem
– Example: HIPO, Stepwise refinement, iterative stepwise refinement, information hiding
• Data-oriented
– Emphasizing on the characteristics of the data processed
• Data-flow oriented: modules according to the type of data elements
• Data-structure oriented: structure of the input and output
• Prescriptive
– Usually provided by the manufacturer of the software
9. Tool for developing a system
• Shaped graph: HIPO, SADT,
• Tools that use the chart:
1. Activity charting: describes the activity, for example: Gant chart, flowchart, etc.
2. Layout charting: Describes the layout
3. Personal relationship charting: describes the relationship of personnel, for example: organization charts, work distribution chart
10. Techniques used for the development of the system include:
Engineering Project Management: CPM, pert
Technical Fact Finding: Interview, Observation, questionnaire, Sampling
Engineering Cost Analysis
Technical Running Meetings
Technical Inspection
11. System analyst & programmer
Systems analyst is a person who analyzes the system with learning
problems that arise and determine the needs of users and
identify solutions that reasonless (better understand the aspects
business and computer technology).
Programmer who is writing code for an application program
based on a design made by the system analysts (better understand
computer technology).
Analysts duty system bridge the knowledge gap that occurs between the user and system programmers.
Knowledge that is required
• Technology data processing, computer programming and
• Knowledge of general business
• quantitative methods: regression, linier programming, etc.
• problem-solving expertise
• Skills of communication between personnel
• Expertise foster relationships between personnel
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Waterfall_model
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spiral_model


Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar